The financial impact of global cybercrime is expected to reach a horrendous amount of USD 6 trillion in 2021 and can increase to USD 10.5 trillion annually by the year 2025. (1)
Terrifying, isn’t it?
Cybercrime is turning out to be a pressing issue for businesses worldwide.
The advanced businesses that deal with a lot of data are at the top of the vulnerability risks. From malicious viruses, malware, denial of services’ attacks, ransomware attacks to the latest Solorigate attack – the one that took place on the SolarWinds software and affected a lot of related organizations, the cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly evolving.
The attacks are becoming more sophisticated and are well-funded. This means the attackers are capable to use advanced technologies to break into the strongest of the security systems. All they need is a weak door.
As cybersecurity evolves, it is important for you as an organization or individual users to be aware of the latest cybersecurity trends.
Let’s look at the top 10 cybersecurity trends to watch out for in 2021.
Top 10 cybersecurity trends
1. Cloud, 5G, IoT threats are witnessing an increase
The rise in technologies like Cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, Artificial Intelligence, etc. is no doubt helping the world become more interconnected. However, the primary downside to this growth is the increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks.
Cloud has emerged as an ally for businesses worldwide by allowing them to shift their operations beyond the physical boundaries of their premises. While global businesses were already adopting cloud at an increasing rate, the pandemic has acted as a catalyst for the same. However, rapid cloud migration is set to trigger a host of new security challenges and threats in 2021.
Organizations will need to amp up their cloud’s security measures and continuously monitor and update applications to safeguard against any data leaks. Cloud services from Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are though equipped with security measures from their end, the end responsibility lies with the users.
Major cloud security threats include access to cloud storage, data breaches and leaks, data loss, and insecure APIs.
According to Trustwave Global Security Report 2020(2), the volume of attacks on cloud-based services more than doubled in 2019 and accounted for nearly 20% of all investigated incidents.
2. Zero trust networks are finding increased acceptance
With increasing threats from both within and outside an organization, traditional security architecture models tend to be inadequate.
According to Gartner, the zero-trust architecture model can be defined as a digital identity-based perimeter with four primary capabilities – identity-based schema, continuous trust evaluation, resource secure access, and adaptive access control.
It helps organizations establish a solid network security architecture with dynamic authorization, comprehensive identity, management automation, and risk measurement.
You might relate a Zero trust architecture (ZTA) to a Virtual Private Network (VPN); however, it is different from that. ZTA is much more secure when it comes to defining policies and controlling remote access to specific applications.
In ZTA, organizations can identify a ‘protect surface’ – which is made up of their most critical and valuable data, assets, applications, and services. They may be unique to every organization. It is identified within an organization i.e., the organization is well aware of how traffic is flowing within the protected surface, ensuring secure access to it.
According to Gartner, 80% of new digital business applications will be accessed through ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) by 2020, and 60% of enterprises will move from remote-access VPNs to ZTNA by 2023.
3. Work from home (WFH) threats are rising
The pandemic has completely changed how work is done and more importantly from where it is done. With a large number of organizations switching to a flexible or remote working model, security experts predict a rise in cyberattacks targeted at the weak and unidentified home networks.
Take a look at this image below that covers the top WFH cybersecurity concerns of organizations. This is an extract from the “Enduring from home: COVID-19’s impact on business security” report by Malwarebytes (3). 45% of the respondents consider devices at home to be unsafe and at a greater risk of being compromised.

Source: Malwarebytes
Threat actors are prepared to take advantage of current working situations and exploit those who are the most susceptible.
As work changes, organizations too will need to update their security policies. They must come up with solutions to protect their remote workers from cyber threats.
Remember, even the most secure system can fail if your employees are not aware of the security threats and their role in keeping the company’s information safe and secure.
Hence, cyber-awareness can be one of the popular cybersecurity trends this year and organizations must start investing in cybersecurity training, especially for those who are working from home. After all, all it takes is one wrong click to compromise your company’s entire network.
4. Patch management software will see good growth
Unpatched vulnerabilities are the most common points of entry exploited by the cyber threat actors during a cyber-attack. They are going to be one of the most talked-about cybersecurity trends this year. Patch management primarily involves fixing any vulnerabilities on software or application that might be exploited by cyber-criminals.
With increasing cyberattack incidents based on exposed vulnerabilities and unpatched systems, patch management is an important cybersecurity trend to look forward to, this year.
A good patch management program like Avast Business Patch Management will help you regularly and timely identify unpatched software and take remedial actions to close the security gaps as soon as possible.
5. Supply chain attacks have become more sophisticated
The recent attack on the SolarWinds Orion platform brought global attention to the need for businesses to make cybersecurity a top priority in 2021.
A single attack on a third-party vendor compromised the data of multiple government and private organizations associated with the victim. This is probably the major reason why supply chain attacks are increasing at an alarming rate.
One point of failure can open multiple attack pathways. Attackers look for the weakest link in your supply chain network. They may be companies with fewer security measures. Below is the visual representation of rising supply chain attacks revealed in a report by the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC).
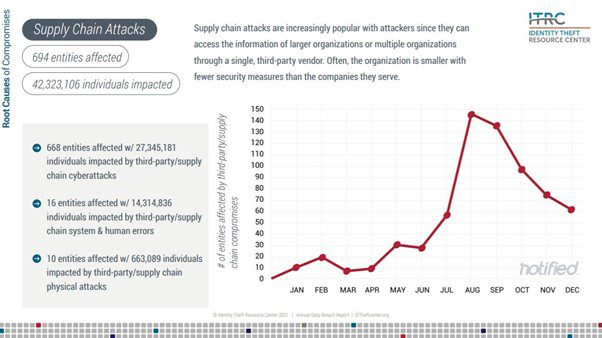
Source: ITRC
6. Ransomware is still the #1 cyber attack
News stories covering ransomware attacks have been hitting the headlines for many years. The trend does not seem to be ending this year as well.
Cybersecurity experts still consider ransomware as one of the most prominent types of cyberattack that is a serious concern for organizations worldwide. The issue will not be magically resolved. It requires organizations to take effective steps to improve their security status.
Ransomware attacks are highly targeted. As the ransom is demanded in bitcoins, it becomes difficult to track the real culprits. Moreover, there is no guarantee that the hacker will share the decryption key once he gets the ransom. Their objective is only to extract money out from you. Don’t expect them to give great customer service. ?
So, the best way here is to take all precautionary measures and train your employees on how to not fall prey to ransomware attacks.
7. Having Security Service Centers will soon become the norm
Security service centres (SOC) refers to a facility that includes an information security team that continuously monitors and analyses an organization’s security posture. It may be a third-party or a centralized function within an organization.
You can think of it as a central security hub that keeps track across an organization’s entire IT infrastructure – devices, networks, appliances, etc.
They keep a stock of all available resources with a clear view of how information, data, and assets flow within and outside the company’s network.
Continuous network monitoring helps the SOC team to be aware of even slight anomalies. It is a viable option for small and medium-sized organizations that cannot afford to hire a full-time internal security team. Large enterprises normally have their own internal SOC.
According to the Marketsandmarkets report, the SOC service market is expected to grow to $1.6 billion by 2025 from $471 million in 2020.
Suggested Reading: Top 11 Cyber Protection Solutions for Businesses – a comparison
8. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) framework is being adopted
Research firm Gartner defines SASE as a security framework designed to enable secure and faster cloud adoption. It ensures that both users and devices have secure cloud access to applications, data, and services from anywhere and anytime.
With increasing cloud adoption, the traditional enterprise framework defined within a physical location is diminishing, giving way to a dynamic set of edge capabilities that can be delivered as a service from the cloud.
This new framework also makes organizations rethink their risk and security management policies. SASE tends to help organizations adopting this new framework by combining networking and network security into a single, cloud-delivered service to support their digital transformation goals and ensure workforce mobility.
9. Automotive hacking is on the rise
The automotive hacking concept would have sounded straight out of a sci-fi movie, a few years back, but not today. As cars and other vehicles become smart, thanks to technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Bluetooth, Wireless, IoT devices, etc. automotive hacking is set to become a top cybersecurity trend in 2021.
Car hacking can take place when a hacker exploits a weakness in an automobile’s communication systems, software, or even hardware components and gains unauthorized access to it. Modern cars contain several computerized types of equipment like a controlled area network (CAN), key fob entry, etc. that can be attacked in multiple ways.
Attackers can also use it to control an automated vehicle – engage the breaks, steer it, or change gears. Vehicle manufacturers have started researching more on automotive cyberattacks and what measures can be taken to curb them.
Automotive related cyber-incidents doubled in 2019 as compared to the previous year (a 605% increase from 2016). (4)
10. Insider threats are now more pronounced
Human errors remain to be one of the most common cybersecurity trends to look out for this year.
This becomes more critical today as companies shift their workforce to a remote working model. As employees work from home or use their own devices to log into company accounts, they are at constant risk of being targeted by bad actors.
Weak passwords, unauthorized access, unsecured networks, etc. are the top concerns organizations should work upon to improve the system security of their remote employees.
Insider threats constitute those employees who either are careless or have no idea that how their actions can compromise their company’s security or the ones who have legitimate user access to the company’s data and wilfully extract it and exchange it with third-party users.
According to Forrester, insider data breaches are poised to increase by 8% in 2021 and account for 33% of all cybersecurity incidents.
Bottom-line
Preparing and securing against cyberattacks have now become strategically important for organizations. Cyber-attacks can ruin your company’s position in the market and make it difficult for the customers to trust you again.
While you cannot rule out their presence entirely, you can take steps to protect your company’s data. And you might start by being aware of what’s trending in the cybersecurity space.
Do you have anything to add to our cybersecurity trends’ list? Do let us know in the comments section below.
Sources:
- 1https://www.business2community.com/cybersecurity/40-terrifying-cybersecurity-statistics-you-need-to-know-for-2021-02384223
- 2https://www.trustwave.com/en-us/resources/library/documents/2020-trustwave-global-security-report/
- 3https://resources.malwarebytes.com/files/2020/08/Malwarebytes_EnduringFromHome_Report_FINAL.pdf
- 4 Upstream Security








